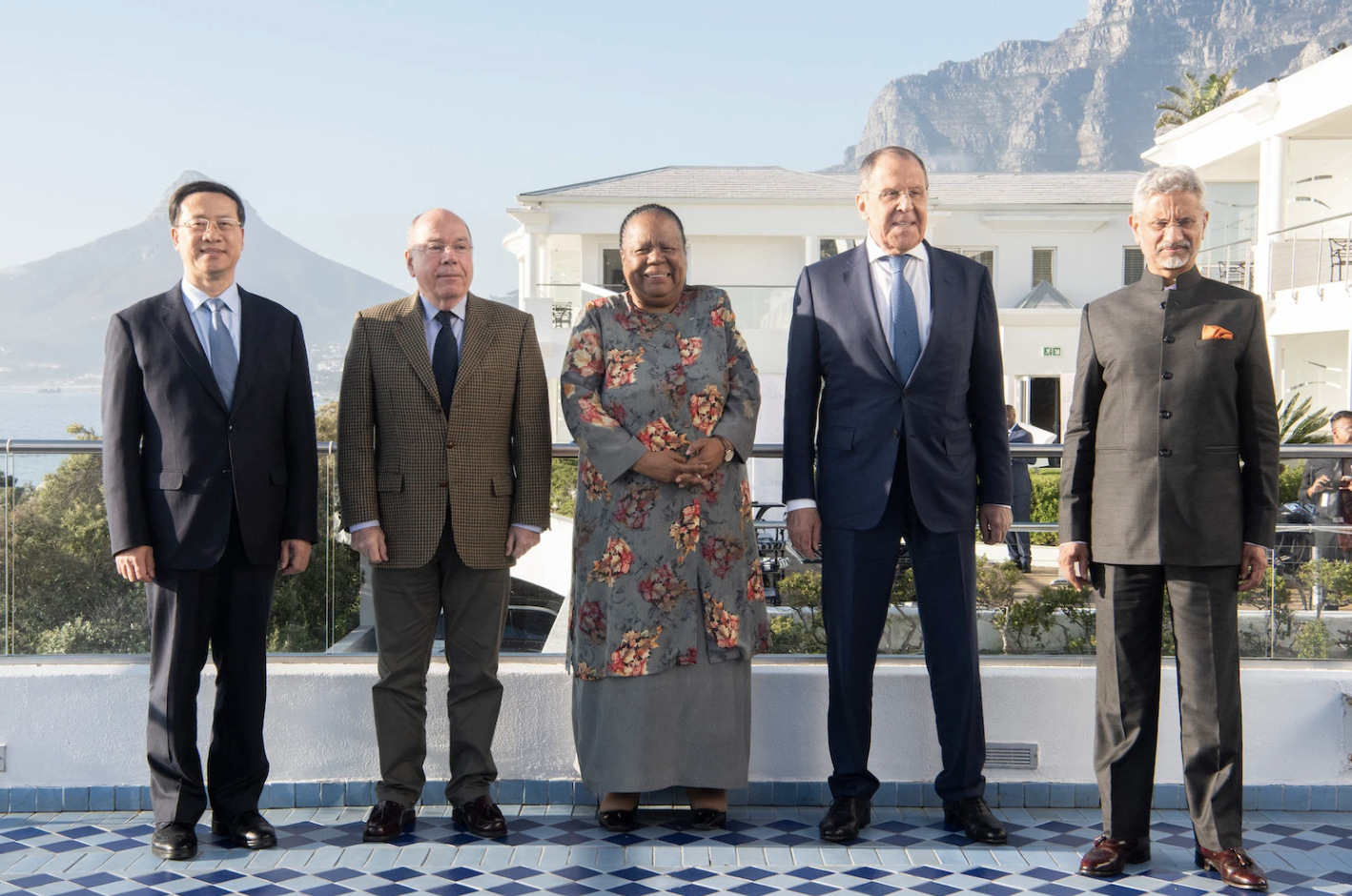
Enlargement would be a sign not of the group’s strength, but of China’s growing influence.
By Oliver Stuenkel, an associate professor of international relations at the Getulio Vargas Foundation in São Paulo
In 2001, Goldman Sachs banker Jim O’Neill created the acronym “BRIC” to refer to Brazil, Russia, India, and China—countries he predicted would soon have a significant impact on the global economy. In 2006, Goldman Sachs opened a BRIC investment fund pegged to growth in these four nations. The moniker captured the global excitement about emerging powers at the time and transformed into a political grouping in 2009, when leaders of the four countries held their first summit. South Africa joined a year later.
BRICS as a political body has faced countless critics and doubters from the start. Analysts in the Western press largely described the outfit as nonsensical and predicted its imminent demise. In 2011, the Financial Times’ Philip Stevens announced it was “time to bid farewell” to the “BRICS without mortar.” A year later, another columnist at the paper, Martin Wolf, asserted that BRICS was “not a group” and that its members had “nothing in common whatsoever.” BRICS has also been described as a “motley crew,” “odd grouping,” “random bunch,” and “disparate quartet.” In 2015, Goldman Sachs decided to close the BRIC fund (which never grew to include South Africa) due to its low returns.
BRICS member countries have numerous differences and disagreements. While Brazil and Russia are commodity exporters, China is a commodity importer. Brazil, India, and South Africa are democratic countries with vibrant civil societies, but…
Read full article here